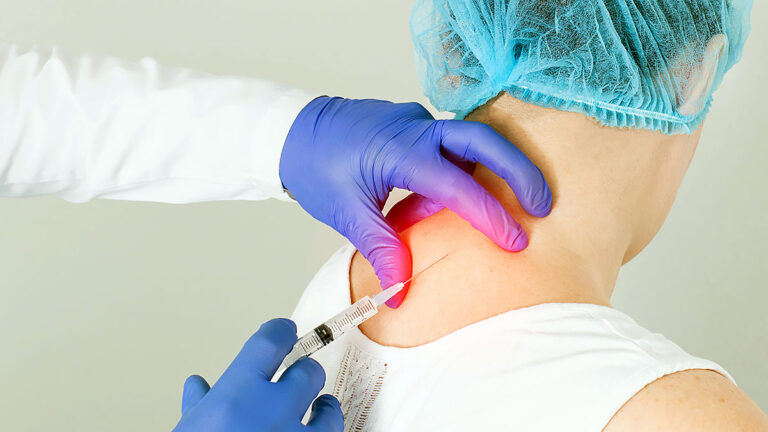
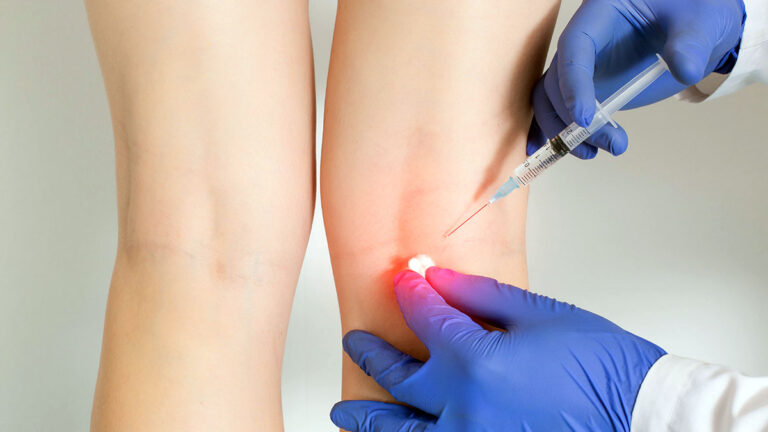
Sympathetic nerve blocks are a powerful, minimally invasive treatment option for managing chronic pain conditions involving the autonomic nervous system. These injections can interrupt pain signals and provide meaningful relief by targeting the sympathetic nerves, which control involuntary body functions like blood pressure, heart rate, and temperature regulation.
This procedure is especially effective for conditions such as Complex Regional Pain Syndrome (CRPS), sympathetically maintained pain, neuropathic pain, and specific cancer-related or vascular pain syndromes.
What Is a Sympathetic Nerve Block?
A sympathetic nerve block involves injecting a local anesthetic (sometimes combined with a corticosteroid) near a cluster of sympathetic nerves to “block” or dampen pain signals traveling through the nervous system. Depending on the affected region of the body, the injection site may vary:
- Stellate Ganglion Block – targets nerves in the neck (for upper extremity, head, and face pain)
- Lumbar Sympathetic Block – targets nerves in the lower back (for pain in the legs, pelvis, or lower abdomen)
- Celiac Plexus Block – used for abdominal or cancer-related pain
The procedure is typically performed under fluoroscopic or ultrasound guidance to ensure precision and safety.
Conditions Treated with Sympathetic Nerve Blocks
Sympathetic blocks are used to treat a range of painful disorders, including:
- Complex Regional Pain Syndrome (CRPS I & II)
- Sympathetically Mediated Pain
- Post-Herpetic Neuralgia
- Peripheral Neuropathy
- Phantom Limb Pain
- Lumbar Radiculopathy
- Cancer Pain (pancreatic, pelvic, or abdominal)
- Refractory Angina (as a non-cardiac pain intervention)
Benefits of Sympathetic Nerve Blocks
Patients suffering from chronic or treatment-resistant pain may benefit from:
Targeted Pain Relief – Blocks pain signals from reaching the brain
Improved Functionality – Reduces inflammation, allowing better movement and daily performance
Minimally Invasive – No need for open surgery; performed with local anesthesia
Outpatient Procedure – Most patients go home the same day
Fewer Side Effects – Localized treatment avoids the systemic impact of oral medications
Repeatable & Customizable – Can be tailored to specific nerves, regions, and patient needs
How the Procedure Works
- Preparation: The treatment area is sterilized, and a local anesthetic is applied to the skin.
- Imaging Guidance: Your provider guides a fine needle to the targeted sympathetic ganglion using fluoroscopy or ultrasound.
- Injection: Medication is delivered directly to the nerve cluster to interrupt pain transmission.
- Monitoring: Patients are observed briefly for response and side effects before discharge.
Most procedures take 30–60 minutes.
Effectiveness & Research Support
Numerous clinical studies support the safety and efficacy of sympathetic nerve blocks:
- A 2017 review in Pain and Therapy found significant improvements in pain relief and functional ability in CRPS patients treated with sympathetic blocks.
- A 2019 Regional Anesthesia & Pain Medicine study reported reduced pain in lumbar radiculopathy patients after sympathetic nerve intervention.
- A 2016 publication in Pain Medicine demonstrated the benefits of sympathetic blocks for post-herpetic neuralgia and other nerve-related pain syndromes.
These findings highlight sympathetic nerve blocks as a viable option when standard treatments like medications or physical therapy fall short.
Are You a Candidate?
Ideal candidates include individuals who:
- Suffer from chronic neuropathic or sympathetically maintained pain
- Have not responded to conservative treatments
- Need relief from pain disrupting daily function or sleep
- Seek a less invasive alternative to surgery
A consultation with a pain specialist at Allied Spine Institute will determine if a sympathetic nerve block is right for you based on your diagnosis, history, and goals.
Risks & Considerations
While generally safe, sympathetic nerve blocks carry some minor risks:
- Bleeding or infection at the injection site
- Temporary numbness or weakness
- Allergic reaction to anesthetic
- Short-lived pain flare-up post-procedure
Relief may be temporary, and some patients require repeat injections every few months for ongoing symptom management.
A Key Part of Comprehensive Pain Management
Sympathetic nerve blocks may be one component of an integrated pain management plan. When combined with:
- Physical therapy
- Behavioral support
- Anti-neuropathic medications
- Complementary treatments (acupuncture, nerve stimulation)
…patients often achieve longer-lasting relief and improved overall outcomes.
Request an Evaluation
If you’re experiencing CRPS, nerve pain, or unresolved chronic pain that hasn’t responded to medication or physical therapy, a sympathetic nerve block could offer the breakthrough you need.